Macromolecule References
OptiPrep™ Reference List RM01
Analysis of plasma lipoproteins
- This OptiPrep™ Reference List contains a brief summary of the methodology for the isolation and analysis of these particles (Section 1); the main aim of this Reference List however is to provide, in Section 2, a comprehensive list of references that report the use of OptiPrep™ for the fractionation of VLDL, LDL and HDL and also LDL and HDL sub-classes. The reference list (Section 1c) at the end of Section 1 applies only to this section.
1. Methodological review
1a. Separation and analysis of VLDL, LDL and HDL
Although ultracentrifugation is regarded as the “gold standard” method for the fractionation of plasma lipoproteins, the traditional method of sequential flotation by incrementally increasing the density of the plasma with KBr to provide sequentially VLDL, LDL and HDL is technically simple but excessively tedious (requiring approx. 3 days). The alternative approach involves the use of either discontinuous or continuous KBr/NaCl gradients; these gradients are technically very difficult to produce and handle. Detailed descriptions of the methodologies can be found in references 1-5. Moreover use of some add-on analytical techniques often necessitates removal of the salt by dialysis, adding up to 12 h to the procedure. Moreover, the use of high salt concentrations may cause the loss of certain surface apoproteins from lipoproteins.
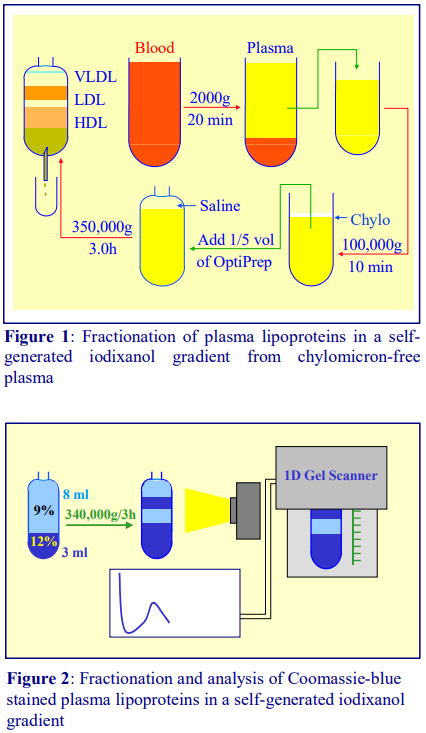 The introduction of self-generated gradients of iodixanol in 1996 [6,7] solved many of the problems associated with earlier technology. A simple one step centrifugation for 3 h that resolves VLDL, LDL and HDL, avoiding the use of technically-difficult salt gradients is summarized in Figure 1. Chylomicron-free plasma is simply mixed with OptiPrep™, transferred to tube for a near-vertical rotor; overlayered with a little saline to fill the tube and centrifuged for 3 h. During the centrifugation the shallow resolving gradient is formed and the lipoproteins move to their banding density. The gradient may be collected as shown in Figure 1 by tube puncture or by aspiration from the meniscus.
The introduction of self-generated gradients of iodixanol in 1996 [6,7] solved many of the problems associated with earlier technology. A simple one step centrifugation for 3 h that resolves VLDL, LDL and HDL, avoiding the use of technically-difficult salt gradients is summarized in Figure 1. Chylomicron-free plasma is simply mixed with OptiPrep™, transferred to tube for a near-vertical rotor; overlayered with a little saline to fill the tube and centrifuged for 3 h. During the centrifugation the shallow resolving gradient is formed and the lipoproteins move to their banding density. The gradient may be collected as shown in Figure 1 by tube puncture or by aspiration from the meniscus.
1b. Separation and analysis of LDL subclasses
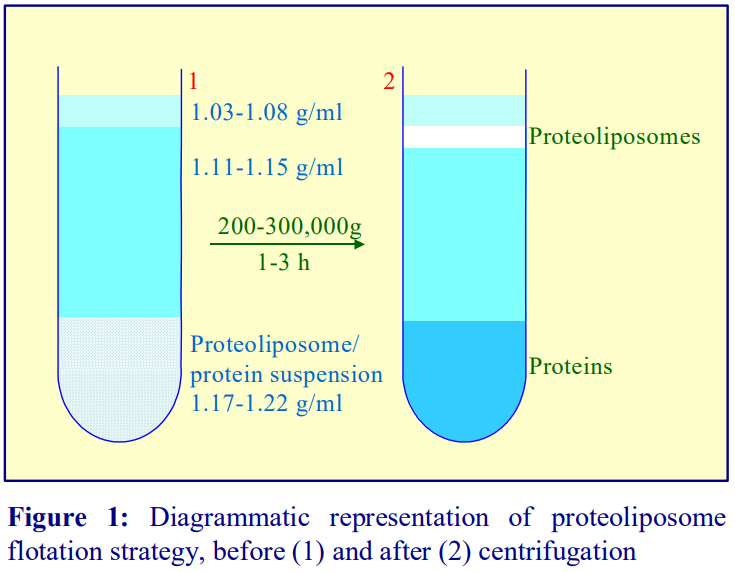
By a small modulation in the starting format, the gradient may be adapted to the fractionation of LDL subclasses; the plasma is adjusted to 12% (w/v) iodixanol (as recommended in refs 6 and 7) but it is overlayered by a solution of 9% (w/v) iodixanol. In a small volume near-vertical rotor such as the Beckman TLN100 the volumes of plasma/12% iodixanol and 9% iodixanol are equal [8]. In the larger volume NVT65 the volumes of 3 ml and 8 ml respectively allow a better resolution of the denser LDL from the HDL [9] and the low density region of the gradient is more shallow , allowing a greater linear separation of the LDL subclasses. In Figure 2 the (3ml + 8 ml) configuration is shown in conjunction with the use of a Coomassie blue stained plasma sample; this allows a density profile of the LDL band to be produced by scanning a digital photograph of the tube assessed without unloading the gradient or assaying the fractions for cholesterol and/or triacylglycerol.
- This strategy has been adapted to the analysis of HDL subclasses in a Sudan black stained plasma [10]
- Detailed protocols for the purification and analysis of the VLDL, LDL and HDL and for the analysis of LDL subclasses are contained in Application Sheets M07 and M08 respectively. The Application Sheets can be accessed from the “Macromolecules and Macromolecular Complex Index” section. Other OptiPrep™ Application Sheets on the preparation of self-generated gradients and harvesting of gradients may also be accessed from the top of the Index.
1c. References
1. Mackness, M. and Durrington, P.N. (1992) Lipoprotein separation and analysis for clinical studies In: Lipoprotein Analysis: A Practical Approach (eds. Converse, C.A. and Skinner, E.R.) IRL Press at Oxford University, Oxford, UK, pp 1-42
2. Lindren, F.T., Jensen, L.C. and Hatch, F.T. (1979) Isolation and quantitative analysis of serum lipoproteins In: Blood lipids and lipoproteins, quantitation, composition and metabolism (ed. Nelson, G.J.) R.E. Krieger Publishing Co. Huntington, NY, pp181-274
3. Chapman, M., Goldstein, J., Lagrange, D. and Laplaud P.M. (1986) A density gradient ultracentrifugation procedure for the isolation of the major lipoprotein classes from human serum J. Lipid Res., 22, 339-358
4. Kelley, J.L. and Kruski, A.W. (1986) Density gradient ultracentrifugation of serum lipoproteins in a swinging bucket rotor Methods Enzymol., 128, 170-181
5. Hinton, R.H., Al-Tamer, Y., Mallinson, A. and Marks, V. (1974) The use of density gradient centrifugation for the separation of serum lipoproteins Clin. Chim. Acta, 53, 355-360
6. Graham, J.M., Higgins, J.A. and Gillot, T. (1995) A new method for the rapid separation of plasma lipoproteins Atherosclerosis, 115 (Supp. l), S123
7. Graham, J., Higgins, J. A., Gillott, T., Taylor, T., Wilkinson, J., Ford, T. and Billington, D. (1996) A novel method for the rapid separation of plasma lipoproteins using self-generated gradients of iodixanol Atherosclerosis, 124, 125-135
8. Sawle, A., Higgins, M.K., Olivant, M.P. and Higgins, J.A. (2002) A rapid single-step centrifugation method for determination of HDL, LDL, and VLDL cholesterol, and TG, and identification of predominant LDL subclass J. Lipid Res., 43, 335-343
9. Davies, I.G., Graham, J.M. and Griffin, B.A. (2003) Rapid separation of LDL subclasses by iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation Clin. Chem., 49, 1865-1872
10. Harman, N.L., Davies, I.G. and Griffin, B.A. (2007) Separation of the principal HDL subclasses by iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation Atherosclerosis, 194, 283
2. Bibliography
Section 2a lists references reporting studies on plasma lipoproteins and is subdivided alphabetically into animal species (e.g. 2a-1 Black bear). The majority of papers are concerned with human plasma lipoproteins (2a-5); this section is subdivided into those concerned with major HDL, LDL and VLDL classes (2a-5-1), HDL subclasses (2a-5-2) and LDL subclasses (2a-5-3). Within Sections 2a-5-1 and 2a-5-2, references are further divided according to research topic, listed alphabetically. A reference may appear in two or more of these research topic subsections. Section 2b lists references reporting the analysis of lipoproteins from sources other than plasma. Within all sections references are listed alphabetically according to first author and chronologically for multiple papers from the same first author.
2a Plasma lipoproteins
2a-1 Black bear
Frank, N., Elliott, S.B., Allin, S.B. and Ramsay, E.C. (2006) Blood lipid concentrations and lipoprotein patterns in captive and wild American black bears (Ursus americanus) Am. J. Vet. Res., 67, 335-341
2a-2 Bovine
Gardner, R.S., Ogden, N.H., Cripps, P.J. and Billington, D. (2003) Separation of bovine plasma lipoproteins by a rapid ultracentrifugation method J. Comp. Path., 128, 15 23
2a-3 Fish
Aas, G.H., Bjerkeng, B., Storebakken, T. and Ruyter, B. (1999) Blood appearance, metabolic transformation and plasma transport proteins of 14C-astaxanthin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) Fish Physiol. Biochem., 21, 325-334
Aursnes, I.A.S., Gjoen,T. and Rishovd, A-L. (2009) Effect of hyperthermia on plasma lipids and gene expression in Atlantic Cod (Gadus Morhua I.) Toxicol. Lett., 189S, S192
Magnoni, L. and Weber, J-M. (2007) Endurance swimming activates trout lipoprotein lipase: plasma lipids as a fuel for muscle J. Exp. Biol., 210, 4016-4023
Prindiville, J.S., Mennigen, J.A., Zamora, J.M., Moon, T.W. and Weber, J-M. (2011) The fibrate drug gemfibrozil disrupts lipoprotein metabolism in rainbow trout Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 251, 201–208
2a-4 Hamster
Bennett, A.J., Kendrick, J.S., Anderton, K.L., Higgins, J.A. and White, D.A. (1997) Effect of dietary fish oil or sunflower oil on plasma lipoproteins and hepatic gene expression in the hamster Atherosclerosis, 130 (Suppl. 1), S24
2a-5 Human
2a-5-1 HDL/LDL/VLDL
Acrolein effects
Conklin, D.J., Barski, O.A., Lesgards, J-F., Juvan, P., Rezen, T., Rozman, D., Prough, R.A., Vladykovskaya, E., Liu, S-Q., Srivastava, S. and Bhatnagar, A. (2010) Acrolein consumption induces systemic dyslipidemia and lipoprotein modification Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 243, 1–12
ApoB fusion proteins
Thierer, J.H., Ekker, S.C. and Farber, S.A. (2019) The LipoGlo reporter system for sensitive and specific monitoring of atherogenic lipoproteins Nat. Comm., 10: 3426
Apolipoprotein(a)
Oliveira, C., Fournier, C., Descamps, V., Morel, V., Scipione, C.A., Romagnuolo, R., Koschinsky, M.L., Boullier, A., Marcelo, P. et al (2017) Apolipoprotein(a) inhibits hepatitis C virus entry through interaction with infectious particles Hepatology, 65, 1851-1864
Apolipoprotein B100
Mason, R.P., Sherratt, S.C.R. and Jacob, R.F. (2016) Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits oxidation of apoBcontaining lipoprotein particles of different size in vitro when administered alone or in combination with atorvastatin active metabolite compared with other triglyceride-lowering agents J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 68, 33–40
Rabbani, N., Chittari, M.V., Bodmer, C.W., Zehnder, D., Ceriello, A. and Thornalley, P.J. (2010) Increased glycation and oxidative damage to apolipoprotein B100 of LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and effect of metformin Diabetes, 59, 1038–1045
Astaxanthin
Coral-Hinostroza, G.N., Ytrestøyl, T., Ruyter, B. and Bjerkeng, B. (2004) Plasma appearance of unesterified astaxanthin geometrical E/Z and optical R/S isomers in men given single doses of a mixture of optical 3 and 3’R/S isomers of astaxanthin fatty acyl diesters Comp. Biochem. Biophys. Part C, 139, 99-110
Osterlie, M., Bjerkeng, B. and Liaaen-Jensen, S. (2000) Plasma appearance and distribution of astaxanthin E/Z and R/S isomers in plasma lipoproteins of men after single dose administration of astaxanthin J. Nutr. Biochem., 11, 482-490
Atherosclerosis risk
Bassendine, M., Nielsen, S. and Neely, D. (2016) Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and atherosclerosis risk: a role for low-density immune complexes? Atherosclerosis, 252, e206
Bacteriochlorophylls, in Dandler, J., Wilhelm, B. and Scheer, H. (2010) Distribution of chlorophyll- and bacteriochlorophyll-derived photosensitizers in human blood plasma Photochem. Photobiol., 86, 182–193
Dandler, J., Wilhelm, B. and Scheer, H. (2010) Photochemistry of bacteriochlorophylls in human blood plasma: Pigment stability and light-induced modifications of lipoproteins Photochem. Photobiol., 86, 331–341
CD36, binding to
Alkhatatbeh, M.J., Mhaidat, N.M., Enjeti, A.K., Lincz, L.F. and Thorne, R.F. (2011) The putative diabetic plasma marker, soluble CD36, is non-cleaved, non-soluble and entirely associated with microparticles J. Thromb. Haemost., 9, 844–851
Cholesterol efflux (ABCA1-mediated)
Tavori, H., Fenton, A.M., Plubell, D.L., Rosario, S., Yerkes, E., Gasik, R., Miles, J., Bergstrom, P., Minnier, J., Fazio, S. and Pamir, N. (2019) Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels lower ABCA1 cholesterol efflux capacity J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 104: 4793–4803
Diabetes Type 1
Ceriello, A., Kumar, S., Piconi, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2007) Simultaneous control of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress normalizes endothelial function in type 1 diabetes Diabet. Care 30, 649-654
Ceriello, A., Piconi, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2007) Telmisartan shows an equivalent effect of vitamin C in further improving endothelial dysfunction after glycemia normalizationin type 1 diabetes Diabet. Care, 30, 1694-1698
Ceriello, A., Esposito, K., Ihnat, M., Thorpe, J. and Giugliano, D. (2009) Long-term glycemic control influences the long-lasting effect of hyperglycemia on endothelial function in type 1 diabetes J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 94, 2751–2756
Diabetes Type 2
Anderson, R.A., Evans, M., Ellis, G. R., Graham, J., Morris, K., Jackson, S. K., Lewis, M. J., Rees, A. and Frenneaux, M. P. (2001) The relationships between post-prandial lipaemia, endothelial function and oxidative stress in healthy individuals and patients with type 2 diabetes Atherosclerosis, 154, 475-483
Anderson, R.A., Evans, L.M., Ellis, G.R., Khan, N., Morris, K., Jackson, S.K., Rees, A., Lewis, M.J. and Frenneaux, M.P. (2006) Prolonged deterioration of endothelial dysfunction in response to postprandial lipaemia is attenuated by vitamin C in type 2 diabetes Diabet. Med., 23, 258-264
Anderson, R.A., Evans, L.M., Ellis, G.R., Khan, N., Morris, K., Jackson, S.K., Rees, A., Lewis, M.J. and Frenneaux, M.P. (2006) Prolonged deterioration of endothelial dysfunction in response to postprandial lipaemia is attenuated by vitamin C in type 2 diabetes Diabet. Med., 23, 258-264
Englyst, N.A., Taube, J.M., Aitman, T.J., Baglin, T.P. and Byrne C.D. (2003) A novel role for CD36 in VLDLenhanced platelet activation Diabetes, 52, 1248-1255
Evans, L.M., Anderson, R.A., Davies, J.S., Ellis, G.R., Jackson, S.K., Graham, J., Lewis, M.J., Frenneaux, M.P. and Rees, A. (1999) Ciprofibrate reduces the postprandial generation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and attenuates the associated endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus Atherosclerosis Suppl 154, 434
Evans, L.M., Anderson, R. A., Graham, J., Ellis, G. R., Morris, K., Davies, S., Jackson, S. K., Lewis, M. J., Frenneaux, M. P. and Rees, A. (2000) Ciprofibrate therapy improves endothelial function and reduces postprandial lipemia and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus Circulation, 101, 1773-1779
Gonzàlez, M., Heras, M., Rosales, R., Guardiola, M., Plana, N., Vallvé, J.C., Masana, L. and Ribalta, J. (2016) Increased presence of remnant lipoprotein cholesterol in the HDL of diabetic subjects Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci., 46, 229-232
Neri, S., Calvagno, S., Mauceri, B., Misseri, M., Tsami, A., Vecchio, C., Mastrosimone, G., Di Pino, A., Maiorca, D., Judica, A., Romano, G., Rizzotto, A. and Signorelli, S.S. (2010) Effects of antioxidants on postprandial oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and Type 2 diabetes Eur. J. Nutr., 49, 409–416
Rabbani, N., Chittari, M.V., Bodmer, C.W., Zehnder, D., Ceriello, A. and Thornalley, P.J. (2010) Increased glycation and oxidative damage to apolipoprotein B100 of LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and effect of metformin Diabetes, 59, 1038–1045
Seo, J.A., Kang, M-C., Ciaraldi, T.P., Kim, S.S., Park, K.S., Choe, C., Hwang, W.M., Lim, D.M. et al (2018) Circulating ApoJ is closely associated with insulin resistance in human subjects Metab. Clin. Exp., 78, 155-166
Sidhu, J.S., Cowan, D. and Kaski, J.C. (2004) Effects of rosiglitazone on endothelial function in men with coronary artery disease without diabetes mellitus Am. J. Cardiol., 94, 151-156
Dietary supplements (fish oil)
Mason, R.P. and Sherratt, S.C.R. (2017) Omega-3 fatty acid fish oil dietary supplements contain saturated fats and oxidized lipids that may interfere with their intended biological benefits Biochem. Biophy. Res. Communications 483, 425-429
Rytter, D., Schmidt, E.B., Bech, B.H., Christensen, J.H., Henriksen, T.B. and Olsen, S.F. (2011) Fish oil supplementation during late pregnancy does not influence plasma lipids or lipoprotein levels in young adult offspring Lipids, 46, 1091–1099
Dietary supplements (garlic oil)
Dillon, S.A., Burmi, R.S., Lowe, G.M., Billington, D. and Rahman, K. (2002) Antioxidant properties of aged garlic extract: an in vitro study incorporating human low density lipoprotein Life Sci., 72, 1538-1594
Zhang, X-H., Lowe, D., Giles, P., Fell, S., Board, A. R., Baughan, J. A., Connock, M. J. and Maslin, D. J. (2000) A randomized trial of the effects of garlic oil upon coronary heart disease risk factors in trained male runners Blood Coagulat. Fibrinolysis, 11, 67-74
Ghrelin
Holmes, E., Davies, I., Lowe, G. and Ranganath, L. (2008) Transport of ghrelin and obestatin in plasma 77th Congr. Eur. Atheroscler. Soc., 2008, Istanbul, Abstr. PO6-37
Holmes, E., Davies, I., Lowe, G. and Ranganath, L.R. (2009) Circulating ghrelin exists in both lipoprotein bound and free forms Ann. Clin. Biochem., 46, 514–516
HDL oxidation
Sherratt, S.C.R. and Mason, R.P. (2018) Eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits oxidation of high density lipoprotein particles in a manner distinct from docosahexaenoic acid Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 496, 335-338
Hedgehog proteins
Palm, W., Swierczynska, M.M., Kumari, V., Ehrhart-Bornstein, M., Bornstein, S.R. and Eaton, S. (2013) Secretion and signaling activities of lipoprotein-associated hedgehog and non-sterol-modified hedgehog in flies and mammals PLoS Biol., 11: e1001505
Hepatitis c virus effects
Jammart, B., Michelet, M., Pécheur, E-I., Parent, R., Bartosch, B., Zoulim, F. and Durante, D. (2013) Verylow-density lipoprotein (VLDL)-producing and hepatitis C virus replicating HepG2 cells secrete no more
lipoviroparticles than VLDL-deficient Huh7.5 cells J. Virol., 87, 5065–5080
Oliveira, C., Fournier, C., Descamps, V., Morel, V., Scipione, C.A., Romagnuolo, R., Koschinsky, M.L., Boullier, A., Marcelo, P. et al (2017) Apolipoprotein(a) inhibits hepatitis C virus entry through interaction with infectious particles Hepatology, 65, 1851-1864
Schöbel, A., Rösch, K. and Herker, E. (2018) Functional innate immunity restricts Hepatitis C Virus infection in induced pluripotent stem cell–derived hepatocytes Sci. Rep., 8: 3893
Sun, H-Y., Lin, C-C., Lee, J-C., Wang, S-W., Cheng, P-N., Wu, I-C., Chang, T-T., Lai, M-D., Shieh, D-B., Young, K-C. (2013) Very low-density lipoprotein/lipo-viro particles reverse lipoprotein lipase-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection via apolipoprotein C-III Gut, 62, 1193–1203
Sun, H-Y., Cheng, P-N., Tseng, C-Y., Tsai, W-J., Chiu, Y-C., Young, K-C. (2018) Favouring modulation of circulating lipoproteins and lipid loading capacity by direct antiviral agents grazoprevir/elbasvir or ledipasvir/sofosbuvir treatment against chronic HCV infection Gut, 67, 1342–1350
Hypercholesterolemia
Ruiu, G., Pinach, S., Veglia, F., Gambino, R., Marena, S., Uberti, B., Alemanno, N., Burt, D., Pagano, G., and Cassader, M. (2009) Phytosterol-enriched yogurt increases LDL affinity and reduces CD36 expression in polygenic hypercholesterolemia Lipids, 44, 153–160
Hyperglycemia
Ceriello, A.C., Taboga, C., Tonutti, L., Quagliaro, L., Piconi, L., Bais, B., Da Ros, R. and Motz, E. (2002) Evidence for an independent and cumulative effect of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia on endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress generation Circulation, 106, 1211-1218
Ceriello, A., Quagliaro, L., Piconi, L., Assaloni, R., Da Ros, R., Maier, A., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2004) Effect of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia on circulating adhesion molecules and oxidative stress generation and the possible role of simvastatin treatment Diabetes, 53, 701-710
Ceriello, A., Kumar, S., Piconi, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2007) Simultaneous control of hyperglycemia and oxidative sreess normalizes endothelial function in type 1 diabetes Diabet. Care 30, 649-654
Ceriello, A., Piconi, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2007) Telmisartan shows an equivalent effect of vitamin C in further improving endothelial dysfunction after glycemia normalization in type 1 diabetes Diabet. Care, 30, 1694-1698
Ceriello, A., Esposito, K., Ihnat, M., Thorpe, J. and Giugliano, D. (2009) Long-term glycemic control influences the long-lasting effect of hyperglycemia on endothelial function in type 1 diabetes J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 94, 2751–2756
Hyperlipidemia
Ceriello, A.C., Taboga, C., Tonutti, L., Quagliaro, L., Piconi, L., Bais, B., Da Ros, R. and Motz, E. (2002) Evidence for an independent and cumulative effect of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia on endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress generation Circulation, 106, 1211-1218
Ceriello, A., Quagliaro, L., Piconi, L., Assaloni, R., Da Ros, R., Maier, A., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2004) Effect of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia on circulating adhesion molecules and oxidative stress generation and the possible role of simvastatin treatment Diabetes, 53, 701-710
Hall, W.L., Jeanes, Y.M. and Lodge, J.K. (2005) Hyperlipidemic subjects have reduced uptake of newly absorbed vitamin E into their plasma lipoproteins, erythrocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes, as studied by deuterium-labeled -tocopherol biokinetics J. Nutr., 135, 58-63
Isotachophoresis
Inano, K., Tezuka, S., Miida, T. and Okada, M. (2000) Capillary isotachophoretic analysis of serum lipoprotein using a carrier ampholyte as spacer ion Ann. Clin. Biochem., 37, 708-716 LCAT deficiency
Yee, M.S., Pavitt, D.V., Richmond, W., Cook, H.T., McLean, A.G., Valabhji, J. and Elkeles, R.S. (2009) Changes in lipoprotein profile and urinary albumin excretion in familial LCAT deficiency with lipid lowering therapy Atherosclerosis 205, 528–532
LDL binding to amyloid β
Yeh, F.L., Wang, Y., Tom, I., Gonzalez, L.C. and Sheng, M. (2016) TREM2 binds to apolipoproteins, including APOE and CLU/APOJ, and thereby facilitates uptake of amyloid-Beta by microglia Neuron 91, 328–340
LDL, lycopene levels
Chew, P.Y., Riley, L., Graham, D.L., Rahman, K. and Lowe, G.M. (2012) Does lycopene offer human LDL any protection against myeloperoxidase activity? Mol. Cell. Biochem., 361, 181–187
Graham, D.L., Carail, M., Caris-Veyrat, C. and Lowe, G.M. (2010) Cigarette smoke and human plasma lycopene depletion Food Chem. Toxicol., 48, 2413–2420
LDL oxidation
AnandBabu, K., Sen, P., Angayarkanni, N. (2019) Oxidized LDL, homocysteine, homocysteine thiolactone and advanced glycation end products act as pro-oxidant metabolites inducing cytokine release, macrophage infiltration and pro-angiogenic effect in ARPE-19 cells PLoS ONE 14: e0216899
Ganini, D. and Mason, R.P. (2014) Absence of an effect of vitamin E on protein and lipid radical formation during lipoperoxidation of LDL by lipoxygenase Free Radic. Biol. Med., 76, 61–68
Helming, L., Winter, J. and Gordon, S. (2009) The scavenger receptor CD36 plays a role in cytokine-induced macrophage fusion J. Cell Sci., 122, 453-459
Jantan, I. and Saputri, F.C. (2012) Benzophenones and xanthones from Garcinia cantleyana var. cantleyana and their inhibitory activities on human low-density lipoprotein oxidation and platelet aggregation Phytochemistry 80, 58–63
Nakano, E., Williamson, M.P., Williams, N.H. and Powers, H.J. (2004) Copper-mediated LDL oxidation by homocysteine and related compounds depends largely on copper ligation Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1688, 33-42
Nakano, E., Taiwo, F.A., Nugent, D., Griffiths, H.R., Aldred, S., Paisi, M., Kwok, M., Bhatt, P., Hill, M.H.E., Moat, S. and Powers, H.J. (2005) Downstream effects on human low density lipoprotein of homocysteine exported from endothelial cells in an in vitro system J. Lipid Res., 46, 484-493
Rabbani, N., Chittari, M.V., Bodmer, C.W., Zehnder, D., Ceriello, A. and Thornalley, P.J. (2010) Increased glycation and oxidative damage to apolipoprotein B100 of LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and effect of metformin Diabetes, 59, 1038–1045
Saputri, F.C. and Jantan, I. (2012) Inhibitory activities of compounds from the twigs of Garcinia hombroniana Pierre on human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and platelet aggregation Phytother. Res. 26: 1845-1850
Shanmuganayagam, D., Beahm, M.R., Kuhns, M.A., Krueger, C.G., Reed, J.D. and Folts, J.D. (2012) Differential effects of grape (Vitis vinifera) skin polyphenolics on human platelet aggregation and low-density lipoprotein oxidation J. Agric. Food Chem., 60, 5787−5794
Wahab, N.A., Ahdan, R., Aufa, Z.A., Kong, K.W., Johar, M.H., Shariff, Z.M. and Ismaila, A. (2015) Nutritional values and bioactive components of under-utilised vegetables consumed by indigenous people in Malaysia J. Sci. Food Agric., 95, 2704–2711
LDL, binding to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-9
Galvan, A.M. and Chorba, J.S. (2019) Cell-associated heparin-like molecules modulate the ability of LDL to regulate PCSK9 uptake J. Lipid Res. 60, 71–84
Golder, M., Sarkar, S., Kosenko, T., McPherson, R. and Lagace, T.A. (2014) Examination of factors affecting the association of PCSK9 with low-density lipoprotein particles in human plasma Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 34, A433
Kosenko, T., Golder, M., Leblond, G., Weng, W. and Lagace, T.A., (2013) Low density lipoprotein binds to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-9 (PCSK9) in human plasma and inhibits PCSK9-mediated low density lipoprotein receptor degradation J. Biol. Chem., 288, 8279–8288
Tavori, H., Christian, D., Minnier, J., Plubell, D., Shapiro, M.D., Yeang, C., Giunzioni, I., Croyal, M., Duell, P.B. et al (2016) PCSK9 association with lipoprotein(a) Circ. Res., 119, 29-35
LDL, surface lipid modification
Sargis, R.M. and Subbaiah, P.V. (2003) Trans unsaturated fatty acids are less oxidizable than cis unsaturated fatty acids and protect endogenous lipids from oxidation in lipoproteins and lipid bilayers Biochemistry, 42, 11533-11543
Lipophilic endotoxin
Rose, J.R., Mullarkey. M. A., Christ, W. J., Hawkins, L. D., Lynn, M., Kishi, Y., Wasan, K. M., Peteherych, K. and Rossignol, D. P. (2000) Consequences of interaction of a lipophilic endotoxin antagonist with plasma lipoproteins Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 44, 504-510
Lipoprotein apheresis
Tavori, H., Giunzioni, I., Linton, M.F. and Fazio, S. (2013) Loss of plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) after lipoprotein apheresis Circ. Res., 113, 1290-1295
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] levels
Tavori, H., Fenton, A.M., Plubell, D.L., Rosario, S., Yerkes, E., Gasik, R., Miles, J., Bergstrom, P., Minnier, J., Fazio, S. and Pamir, N. (2019) Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels lower ABCA1 cholesterol efflux capacity J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 104: 4793–4803
LOX-1 receptor
Vohra, R.S., Murphy, J.E., Walker, J.H., Homer-Vanniasinkam, S. and Ponnamabalam, S. (2007) Functional refolding of a recombinant C-type lectin-like domain containing intramolecular disulfide bonds Protein Expr. Purif., 52, 415-421
Lycopene, effects on LDL
Chew, P.Y., Riley, L., Graham, D.L., Rahman, K. and Lowe, G.M. (2012) Does lycopene offer human LDL any protection against myeloperoxidase activity? Mol. Cell. Biochem., 361, 181–187
Metabolic syndrome
Mah, E., Sapper, T.N., Chitchumroonchokchai, C., Failla, M.L., Schill, K.E., Clinton, S.K., Bobe, G., Traber, M.G. and Bruno, R.S. (2015) α-Tocopherol bioavailability is lower in adults with metabolic syndrome regardless of dairy fat co-ingestion: a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 102, 1070–
Methodology
Billington, D., Maxwell, E., Graham, J.M. and Newland, P. (2007) Large-scale preparation of human low- and high-density lipoproteins by density gradient centrifugation using iodixanol Anal. Biochem., 367, 137-139
Graham, J.M., Higgins, J.A. and Gillot, T. (1995) A new method for the rapid separation of plasma lipoproteins Atherosclerosis, 115 (Suppl), S123
Graham, J., Higgins, J. A., Gillott, T., Taylor, T., Wilkinson, J., Ford, T. and Billington, D. (1996) A novel method for the rapid separation of plasma lipoproteins using self-generated gradients of iodixanol Atherosclerosis, 124, 125-135
Langlois, M.R. and Blaton, V.H. (2006) Historical milestones in measurement of HDL-cholesterol: Impact on clinical and laboratory practice Clin. Chim. Acta, 369, 168-178
Patterson, B. W. (2002) Methods for measuring lipid metabolism in vivo Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care, 5, 475-479
Yee, M.S., Pavitt, D.V., Tan, T., Venkatesan, S., Godsland, I.F., Richmond, W. and Johnston, D.G. (2008) Lipoprotein separation in a novel iodixanol density gradient, for composition, density and phenotype analysis J. Lipid Res., 49, 1364-1371
Microparticles
Alkhatatbeh, M.J., Mhaidat, N.M., Enjeti, A.K., Lincz, L.F. and Thorne, R.F. (2011) The putative diabetic plasma marker, soluble CD36, is non-cleaved, non-soluble and entirely associated with microparticles J. Thromb. Haemost., 9, 844–851
Mitotane binding
Kroiss, M., Plonné, D., Kendl, S., Schirmer, D., Ronchi, C.L., Schirbel, A., Zink, M., Lapa, C. et al (2016) Association of mitotane with chylomicrons and serum lipoproteins: practical implications for treatment of adrenocortical carcinoma Eur. J. Endocrinol., 174, 343–353
Obestatin
Holmes, E., Davies, I., Lowe, G. and Ranganath, L. (2008) Transport of ghrelin and obestatin in plasma 77th Congr. Eur. Atheroscler. Soc., 2008, Istanbul, Abstr. PO6-37
Phytosterols
Ruiu, G., Pinach, S., Veglia, F., Gambino, R., Marena, S., Uberti, B., Alemanno, N., Burt, D., Pagano, G., and Cassader, M. (2009) Phytosterol-enriched yogurt increases LDL affinity and reduces CD36 expression in polygenic hypercholesterolemia Lipids, 44, 153–160
Platelet activation by VLDL
Englyst, N.A., Taube, J.M., Aitman, T.J., Baglin, T.P. and Byrne C.D. (2003) A novel role for CD36 in VLDLenhanced platelet activation Diabetes, 52, 1248-1255
Porphyrin conjugates
Kralova, J., Synytsya, A., Pouckova, P., Koc, M., Dvorak, M. and Kral, V. (2006) Novel porphyrin conjugates with a potent photodynamic antitumor effect: differential efficacy of mono- and bis-β-cyclodextrin derivatives Photochem. Photobiol., 82, 432-438
Postprandial lipaemia
Anderson, R.A., Evans, L. M., Ellis, G. R., Graham, J., Jackson, S. K., Lewis, M. J., Rees, A. and Frenneaux, M. P. (1999) In healthy adults, postprandial lipaemia results in triglyceride enrichment of very low-density lipoprotein, enhanced oxidative stress and deterioration in endothelial function Atherosclerosis Suppl 154, 434
Anderson, R.A., Evans, M., Ellis, G. R., Graham, J., Morris, K., Jackson, S. K., Lewis, M. J., Rees, A. and Frenneaux, M. P. (2001) The relationships between post-prandial lipaemia, endothelial function and oxidative stress in healthy individuals and patients with type 2 diabetes Atherosclerosis, 154, 475-483
Anderson, R.A., Evans, L.M., Ellis, G.R., Khan, N., Morris, K., Jackson, S.K., Rees, A., Lewis, M.J. and Frenneaux, M.P. (2006) Prolonged deterioration of endothelial dysfunction in response to postprandial lipaemia is attenuated by vitamin C in type 2 diabetes Diabet. Med., 23, 258-264
Ceriello, A., Assaloni, R., Da Ros, R., Maier, A., Piconi, L., Quagliaro, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2005) Effect of Atorvastatin and Irbesartan, alone and in combination, on postprandial endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients Circulation, 111, 2518-2524
Evans, L.M., Anderson, R.A., Davies, J.S., Ellis, G.R., Jackson, S.K., Graham, J., Lewis, M.J., Frenneaux, M.P. and Rees, A. (1999) Ciprofibrate reduces the postprandial generation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and attenuates the associated endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus Atherosclerosis Suppl 154, 434
Evans, L.M., Anderson, R. A., Graham, J., Ellis, G. R., Morris, K., Davies, S., Jackson, S. K., Lewis, M. J., Frenneaux, M. P. and Rees, A. (2000) Ciprofibrate therapy improves endothelial function and reduces postprandial lipemia and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus Circulation, 101, 1773-1779
Neri, S., Calvagno, S., Mauceri, B., Misseri, M., Tsami, A., Vecchio, C., Mastrosimone, G., Di Pino, A., Maiorca, D., Judica, A., Romano, G., Rizzotto, A. and Signorelli, S.S. (2010) Effects of antioxidants on postprandial oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and Type 2 diabetes Eur. J. Nutr., 49, 409–416
Proteomics
Sun, H-Y., Chen, S-F., Lai, M-D., Chang, T-T., Chen, T-L., Li, P-Y., Shieh, D-B. and Young, K-C. (2010) Comparative proteomic profiling of plasma very-low-density and low-density lipoproteins Clin. Chim. Acta, 411, 336–344
Rosiglitazone in CAD
Sidhu, J.S., Cowan, D. and Kaski, J.C. (2004) Effects of Rosiglitazone on endothelial function in men with coronary artery disease without diabetes mellitus Am. J. Cardiol., 94, 151-156
Selenoprotein, LDL association
Gao, Y., Pagnon, J., Feng, H.C., Konstanopoulos, N., Jowett, J.B.M., Wlader, K. and Collier, G.R. (2007) Secretion of the glucose-regulated selenoprotein SEPS1 from hepatoma cells Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 356, 636-641
Surfactant effects – perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate
Butenhoff, J.L., Pieterman, E., Ehresman, D.J., Gorman, G.S., Olsen, G.W., Chang, S-C. and Princen, H.M.G. (2012) Distribution of perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate into human plasma lipoprotein fractions Toxicol. Lett., 210, 360– 365
Butenhoff, J.L., Pieterman, E.J., Ehresman, D.J., Olsen, G.W., Chang, S-C., Princen, H.M.G. (2012) Distribution of perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate into human plasma lipoprotein fractions over a wide range of concentrations Reprod. Toxicol., 33 1–29
Surfactant effects – Pneumocyte seceretion
Damas, J.E. and Cake, M.H. (2011) An albumin-associated PLA2-like activity inactivates surfactant phosphatidylcholine secreted from fetal type II pneumocytes Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol., 301, L966–L974
Telmisartan in Type 1 diabetes
Ceriello, A., Piconi, L., Esposito, K. and Giugliano, D. (2007) Telmisartan shows an equivalent effect of vitamin C in further improving endothelial dysfunction after glycemia normalization in type 1 diabetes Diabet. Care, 30, 1694-1698
Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein clearance
Khetarpal, S.A., Zeng, X., Millar, J.S., Vitali, C., Somasundara, A.V.H., Zanoni, P., Landro, J.A., Barucci, N., Zavadoski, W.J., Sun, Z., de Haard, H. et al (2017) A human APOC3 missense variant and monoclonal antibody accelerate apoC-III clearance and lower triglyceride-rich lipoprotein levels Nat. Med., 23, 1086-1094
Vitamin E effects
Hall, W.L., Jeanes, Y.M. and Lodge, J.K. (2005) Hyperlipidemic subjects have reduced uptake of newly absorbed vitamin E into their plasma lipoproteins, erythrocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes, as studied by deuterium-labeled -tocopherol biokinetics J. Nutr., 135, 58-63
Mah, E., Sapper, T.N., Chitchumroonchokchai, C., Failla, M.L., Schill, K.E., Clinton, S.K., Bobe, G., Traber, M.G. and Bruno, R.S. (2015) α-Tocopherol bioavailability is lower in adults with metabolic syndrome regardless of dairy fat co-ingestion: a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 102, 1070–80
VLDL clearance
Deng, Y., Foley, E.M., Gonzales, J.C., Gordts, P.L., Li, Y. and Esko, J.D.(2012) Shedding of syndecan-1 from human hepatocytes alters very low density lipoprotein clearance Hepatology, 55, 277-286
VLDL/hepatitis C interactions
Sun, H-Y., Lin, C-C., Lee, J-C., Wang, S-W., Cheng, P-N., Wu, I-C., Chang, T-T., Lai, M-D., Shieh, D-B., Young, K-C. (2013) Very low-density lipoprotein/lipo-viro particles reverse lipoprotein lipase-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection via apolipoprotein C-III Gut, 62, 1193–1203
Xanthophyll delivery
Thomas, S.E. and Harrison, E.H. (2016) Mechanisms of selective delivery of xanthophylls to retinal pigment epithelial cells by human lipoproteins J. Lipid Res., 57, 1865–1878
2a-5-2 HDL subclasses
Harman, N.L., Davies, I.G. and Griffin, B.A. (2007) Separation of the principal HDL subclasses by iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation Atherosclerosis, 194, 283
Harman, N.L., Griffin, B.A. and Davies, I.G. (2013) Separation of the principal HDL subclasses by iodixanol ultracentrifugation J. Lipid Res., 54, 2273-2281
2a-5-3 LDL subclasses
Algal triacylglycerols
Sanders, T.A.B., Gleason, K., Griffin, B. and Miller, G.J. (2006) Influence of an algal triacylglycerol containing docosahexaenoic acid (22: 6n-3) and docosapentaenoic acid (22: 5n-6) on cardiovascular risk factors in healthy men and women Br. J. Nutr., 95, 525-531
Cardiovascular disease
Hirayama, S. and Miida, T. (2012) Small dense LDL: An emerging risk factor for cardiovascular disease Clin. Chim. Acta, 414, 215–224
Carotenoids
Lowe, G.M., Bilton, R. F., Davies, I. G., Ford, T. C., Billington, D. and Young, A. J. (1999) Carotenoid composition and antioxidant potential in subfractions of human low-density lipoprotein Ann. Clin. Biochem., 36, 323-332
Cholesterol, dietary
Harman, N.L., Leeds, A.R. and Griffin, B.A. (2008) Increased dietary cholesterol does not increase plasma low density lipoprotein when accompanied by an energy-restricted diet and weight loss Eur. J. Nutr., 47, 287-293
Conjugated linoleic acid
Tricon, S., Burdge, G.C., Jones, E.L., Russell, J.L., El-Khazen, S., Moretti, E., Hall, W.L., Gerry, A.B., Leake, D.S., Grimble, R.F., Williams, C.M., Calder, P.C. and Yaqoob, P. (2006) Effects of dairy products naturally enriched with cis-9, trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid on the blood lipid profile in healthy middle-aged men Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 83, 744-753
Coronary angiography
Toft-Petersen, A.P., Tilsted, H.H., Aarøe, J., Rasmussen, K., Christensen, T., Griffin, B.A., Aardestrup, I.V., Andreasen, A. and Schmidt, E.B. (2011) Small dense LDL particles – a predictor of coronary artery disease evaluated by invasive and CT-based techniques: a case-control study Lipids Health Disease 10: 21
Dietary effects
Harman, N.L., Leeds, A.R. and Griffin, B.A. (2008) Increased dietary cholesterol does not increase plasma low density lipoprotein when accompanied by an energy-restricted diet and weight loss Eur. J. Nutr., 47, 287-293
Isherwood, C., Wong, M., Jones, W.S., Davies, I.G. and Griffin, B.A. (2010) Lack of effect of cold water prawns on plasma cholesterol and lipoproteins in normo-lipidaemic men Cell. Mol. Biol. 56, 52-58
Jebb, S.A., Lovegrove, J.A., Griffin, B.A., Frost, G.S., Moore, C.S., Chatfield, M.D., Bluck, L.J., Williams, C.M. and Sanders, T.A.B. (2010) Effect of changing the amount and type of fat and carbohydrate on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk: the RISCK (Reading, Imperial, Surrey, Cambridge, and Kings) trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 92, 748–58
Endothelial dysfunction
Mason, R.P., Dawoud, H., Jacob, R.F., Sherratt, S.C.R. and Malinski, T. (2108) Eicosapentaenoic acid improves endothelial function and nitric oxide bioavailability in a manner that is enhanced in combination with a statin Biomed. Pharmacother., 103, 1231–1237
Rasmussen, J.G., Eschen, R.B., Aardestrup, I.V., Dethlefsen, C., Griffin, B.A. and Schmidt, E.B. (2009) Flowmediated vasodilatation: variation and interrelationships with plasma lipids and lipoproteins Scand., J. Clin. Lab. Invest., 69, 156-160
Fatty acid type
Griffin, M.D., Sanders, T.A.B., Davies, I.G., Morgan, L.M., Millward, D.J., Lewis, F., Slaughter, S., Cooper, J.A., Miller, G.J. and Griffin, B.A. (2006) Effects of altering the ratio of dietary n-6 to n-3 fatty acids on insulin sensitivity, lipoprotein size and postprandial lipemia in men and postmenopausal women aged 45-70 y: the
OPTILIP study Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 84, 1290-1298
Jebb, S.A., Lovegrove, J.A., Griffin, B.A., Frost, G.S., Moore, C.S., Chatfield, M.D., Bluck, L.J., Williams, C.M. and Sanders, T.A.B. (2010) Effect of changing the amount and type of fat and carbohydrate on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk: the RISCK (Reading, Imperial, Surrey, Cambridge, and Kings) trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 92, 748–58
Insulin sensitivity
Jebb, S.A., Lovegrove, J.A., Griffin, B.A., Frost, G.S., Moore, C.S., Chatfield, M.D., Bluck, L.J., Williams, C.M. and Sanders, T.A.B. (2010) Effect of changing the amount and type of fat and carbohydrate on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk: the RISCK (Reading, Imperial, Surrey, Cambridge, and Kings) trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 92, 748–58
Isoflavone effects
Hall, W.L., Vafeiadou, K., Hallund, J., Bugel, S., Reimann, M., Koebnick, C., Zunft, H-J. F., Ferrari, M., Branca, F., Dadd, T., Talbot, D., Powell, J., Minihane, A-M., Cassidy, A., Nilsson, M., Dahlman-Wright, K., Gustafsson, J-A. and Williams, C.M. (2006) Soy-isoflavone-enriched foods and markers of lipid and glucose metabolism in postmenopausal women: interactions with genotype and equol production Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 83, 592-600
Methodology
Chung, M., Lichtenstein, A.H., Ip, S., Lau, J. and Balk, E.M. (2009) Comparability of methods for LDL subfraction determination: A systematic review Atherosclerosis 205, 342–348
Davies, I.G. and Griffin, B.A. (2001) Rapid identification of LDL subclass phenotypes by iodixanol gradient centrifugation Atherosclerosis, 159, 249
Davies, I.G., Graham, J.M. and Griffin, B.A. (2003) Rapid separation of LDL subclasses by iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation Clin. Chem., 49, 1865-1872
Sawle, A., Higgins, M.K., Olivant, M.P., and Higgins, J.A (2002) A rapid single-step centrifugation method for determination of HDL, LDL, and VLDL cholesterol, and TG, and identification of predominant LDL subclass J. Lipid Res., 43, 335-343
Mitotane binding
Kroiss, M., Plonné, D., Kendl, S., Schirmer, D., Ronchi, C.L., Schirbel, A., Zink, M., Lapa, C. et al (2016) Association of mitotane with chylomicrons and serum lipoproteins: practical implications for treatment of adrenocortical carcinoma Eur. J. Endocrinol., 174, 343–353
Obesity/triglycerides/weight loss
Hobkirk, J.P., King, R.F., Davies, I., Harman, N., Gately, P., Pemberton, P., Smith, A., Barth, J.H. and Carroll, S. (2014) The metabolic inter-relationships between changes in waist circumference, triglycerides, insulin sensitivity and small, dense low-density lipoprotein particles with acute weight loss in clinically obese children and adolescents Pediatr. Obes., 9, 209–217
Renal disease
Sørensen, G.V.B., Svensson, M., Strandhave, C., Schmidt, E.B., Jørgensen, K.A. and Christensen, J.H. (2015) The effect of n-3 fatty acids on small dense low-density lipoproteins in patients with end-stage renal disease: a randomized placebo-controlled intervention study J. Renal Nutr., 25, 376-380
Simvastatin effects
Hörl, G., Froehlich, H.F., Ferstl, U., Ledinski, G., Binder, J., Cvirn, G., Stojakovic, T., Trauner, M., Koidl, C. et al (2016) Simvastatin efficiently lowers small LDL-IgG immune complex levels: a therapeutic quality beyond the lipid-lowering effect PLoS One, 11: e0148210
Thai population, in
Kulanuwat, S., Tungtrongchitr, R., Billington, D. and Davies, I.G. (2015) Prevalence of plasma small dense LDL is increased in obesity in a Thai population Lipids Health Dis., 14: 30
2a-6 Mouse
Chylomicron assembly
Kendrick, J.S., Chan, L., and Higgins, J.A. (2001) Superior role of apolipoprotein B48 over apolipoprotein B100 in chylomicron assembly and fat absorption: an investigation of apobec-1 knock-out and wild-type mice Biochem. J., 356, 821-827
Gasoline emissions
Lund, A.K., Knuckles, T.L., Akata, C.O., Shohet, R., McDonald, J.D., Gigliotti, A., Seagrave, J.C. and Campen, M.J. (2007) Gasoline exhaust emissions induce vascular remodeling pathways involved in atherosclerosis Toxicol. Sci., 95, 485-494
HDL, brevetoxin association
Woofter, R.T., Spiess, P.C. and Ramsdell. J.S. (2005) Distribution of brevetoxin (PbTx-3) in mouse plasma: association with high-density lipoprotein Environ. Health Perspect., 113, 1491-1496
LDL Receptor
Tavori, H., Fan, D., Blakemore, J.L., Yancey, P.G., Ding, L., Linton, M.F., Fazio, S. (2013) Serum proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 and cell surface low-density lipoprotein receptor evidence for a reciprocal regulation Circulation, 127, 2403-2413
VLDL assembly
Hesse, D., Radloff, K., Jaschke, A., Lagerpusch, M., Chung, B., Tailleux, A., Staels, B. and Schürmann, A. (2014) Hepatic trans-Golgi action coordinated by the GTPase ARFRP1 is crucial for lipoprotein lipidation and assembly J. Lipid Res., 55, 41–52
VLDL, liver injury
Bergheim, I., Guo, L., Davis, M.A., Lambert, J.C., Beier, J.I., Duveau, I., Luyendyk, J.P., Roth, R.A. and Arteel, G.E. (2006) Metformin prevents alcohol-induced liver injury in the mouse: critical role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 Gastroenterology, 130, 2099-2112
2a-7 Porcine
Soler, L., Molenaar, A., Merola, N., Eckersall, P.D., Gutiérrez, A., Cerón, J.J., Mulero, V. and Niewold, T.A. (2012) Why working with porcine circulating serum amyloid A is a pig of a job J. Theoret. Biol., 317, 119–125
2a-8 Rabbit
Cartwright, I.J. and Higgins, J.A. (2001) Direct evidence for a in the lumen of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of rabbit two-step assembly of ApoB48-containing lipoproteins enterocytes J. Biol. Chem, 276, 48048-48057
Wilkinson J., Higgins, J.A., Fitzsimmons, C. and Bowyer, D.E. (1998) Dietary fish oils modify the assembly of VLDL and expression of the LDL receptor in rabbit liver Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 18, 1490-1497
Wilsie, L.C., Chanchani, S., Navaratna, D. and Orlando, R.A. (2005) Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans contribute to intracellular lipid accumulation in adipocytes Lipids Health Dis., 4, 1-15
Wilsie, L.C., Gonzales, A.M. and Orlando, R.A. (2006) Syndecan-1 mediates internalization of apoE-VLDL through a low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP)-independent, non-clathrin-mediated pathway Lipids Health Dis., 5:23
2a-9 Rat
Blanchard, H., Boulier-Monthéan, N., Legrand, P. and Pédrono, F. (2014) The 51 kDa FADS3 is secreted in the ECM of hepatocytes and blood in rat J.Cell. Biochem., 115, 199–207
2b Lipoproteins from non-plasma sources
2b-1 Caco-2 cells
Bateman, P.A., Jackson, K.G., Maitin, V., Yaqoob, P. and Williams, C.M. (2007) Differences in cell morphology, lipid and apo B secretory capacity in caco-2 cells following long-term treatment with saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1771, 475-485
Jackson, K.G., Bateman, P.A., Yaqoob, P. and Williams, C.M. (2009) Impact of saturated, poly-unsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acid-rich micelles on lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in Caco-2 cells Lipids, 44, 1081–1089
Yang, Y., Xiao, H. and McClements, D.J. (2017) Impact of lipid phase on the bioavailability of vitamin E in emulsion-based delivery systems: relative importance of bioaccessibility, absorption, and transformation J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3946−3955
Yao, M., McClements, D.J., Zhao, F., Craig, R.W. and Xiao, H. (2017) Controlling the gastrointestinal fate of nutraceutical and pharmaceutical-enriched lipid nanoparticles: From mixed micelles to chylomicrons NanoImpact, 5, 13–21
2b-2 Drosophila
Brankatschk, M. and Eaton, S. (2010) Lipoprotein particles cross the blood–brain barrier in Drosophila J. Neurosci., 30, 10441–10447
Eugster, C., Panáková, D., Mahmoud, A. and Eaton, S. (2007) Lipoprotein-heparan sulfate interactions in the Hh pathway Devel. Cell, 13, 57-71
Palm, W., Sampaio, J.L., Brankatschk, M., Carvalho, M., Mahmoud, A., Shevchenko, A. and Eaton, S. (2012) Lipoproteins in Drosophila melanogaster—assembly, function, and influence on tissue lipid composition PLoS Genet., 8: e1002828
2b-3 Hepatocytes
Jammart, B., Zoulim, F. and Durantel, D. (2011) Lipoprotein secretion profiles and VLDL production in hepatocyte cell lines J.Hepatol., 54, S318
Jammart, B., Michelet, M., Pécheur, E-I., Parent, R., Bartosch, B., Zoulim, F. and Durante, D. (2013) Verylow-density lipoprotein (VLDL)-producing and hepatitis C virus replicating HepG2 cells secrete no more lipoviroparticles than VLDL-deficient Huh7.5 cells J. Virol., 87, 5065–5080
Lee, E.M., Alsagheir, A., Wu, X., Hammack, C., McLauchlan, J., Watanabe, N., Wakita, T., Kneteman, N.M., Douglas, D.N. and Tang, H. (2016) Hepatitis C virus-induced degradation of cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector B leads to hepatic lipid dysregulation J. Virol., 90, 4174-4185
2b-4 Ovinefollicular/oviductal fluid
Bernecic, N.C., Gadella, B.M., deGraaf, S.P. and Leahy, T. (2016) Isolation of high density lipoproteins in ovine follicular and oviductal fluid Animal Reprod. Sci., 169, 122-123
2b-5 Polychaete
Schenk, S., Harris, J.R. and Hoeger, U. (2006) A discoidal lipoprotein from the coelomic fluid of the polychaete Nereis virens Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part B, 143, 236-243
Schenk, S. and Hoeger, U. (2010) Lipid accumulation and metabolism in polychaete spermatogenesis: role of the large discoidal lipoprotein Mol. Reprod. Dev., 77, 710–719
OptiPrep™ Reference List RM01; 6th edition, January 2020
OptiPrep™ Reference List RM02
Proteo- and DNA-liposomes – methodology and bibliography
- This OptiPrep™ Reference List contains a brief summary of the methodology for the separation of proteoliposomes from soluble proteins (Section 1); Section 2 contains a list of references (up to mid-2014) that report the use of OptiPrep™; it serves to highlight some of the significant practical variations that have been reported. A list of more recent papers is given in Section 3.
 1. Methodological summary
1. Methodological summary
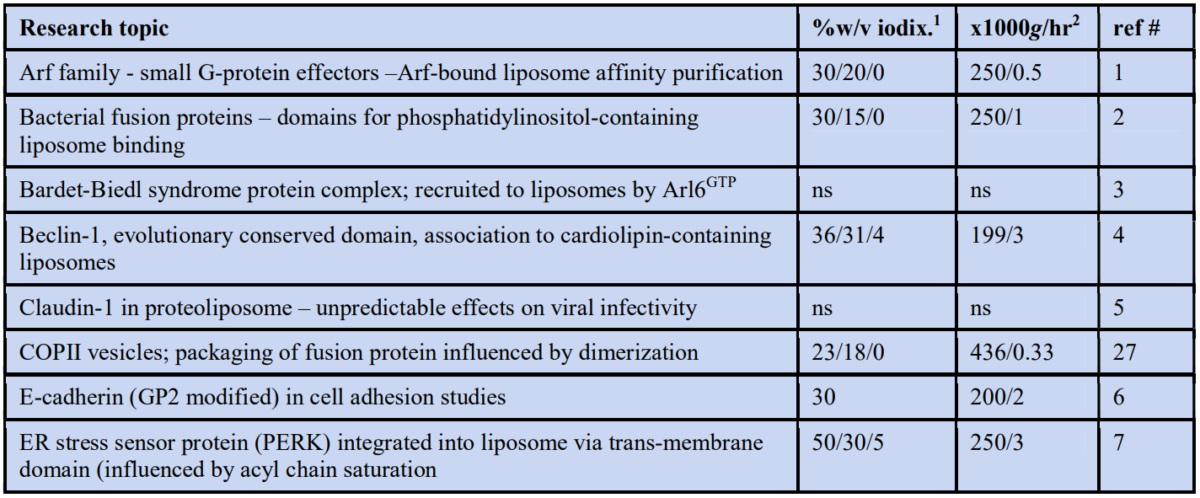
After protein has been incorporated into some form of liposome, it is usually necessary to resolve the newly formed proteoliposomes from any unincorporated protein. The most widely used strategy is described in Figure 1: the sample is adjusted to a density of 1.17-1.22 g/ml (depending on the OptiPrep™ diluent this is approx. equivalent to 30-40% w/v iodixanol) by mixing with a highdensity stock solution and layered beneath two lower density layers. The topmost layer is sometimes the isolation buffer rather than a low density iodixanol solution. During centrifugation the proteoliposomes float up through the 1.11-1.15 g/ml barrier to band at the top interface. The big advantage of this strategy is that the unincorporated protein remains in the sample zone and will even tend to sediment in the opposite direction. If the sample is layered on top of a density barrier the proteoliposomes and the free proteins sediment in the same direction. Depending on the details of the gradient and the centrifugation conditions, the separation may be based either on the difference in density between the proteins and proteoliposomes or the more rapid movement of the larger proteoliposomes.
There are some significant variants to this general strategy, for example the omission of a low-density layer entirely. The reported g-forces also vary quite widely, most are in the 200-300,000 g range but both higher 500,000 g for 1 h and lower 150,000 g for 18 h have been reported. Some of the variations in methodology are listed in the Table in Section 2.
2. Methodological variations
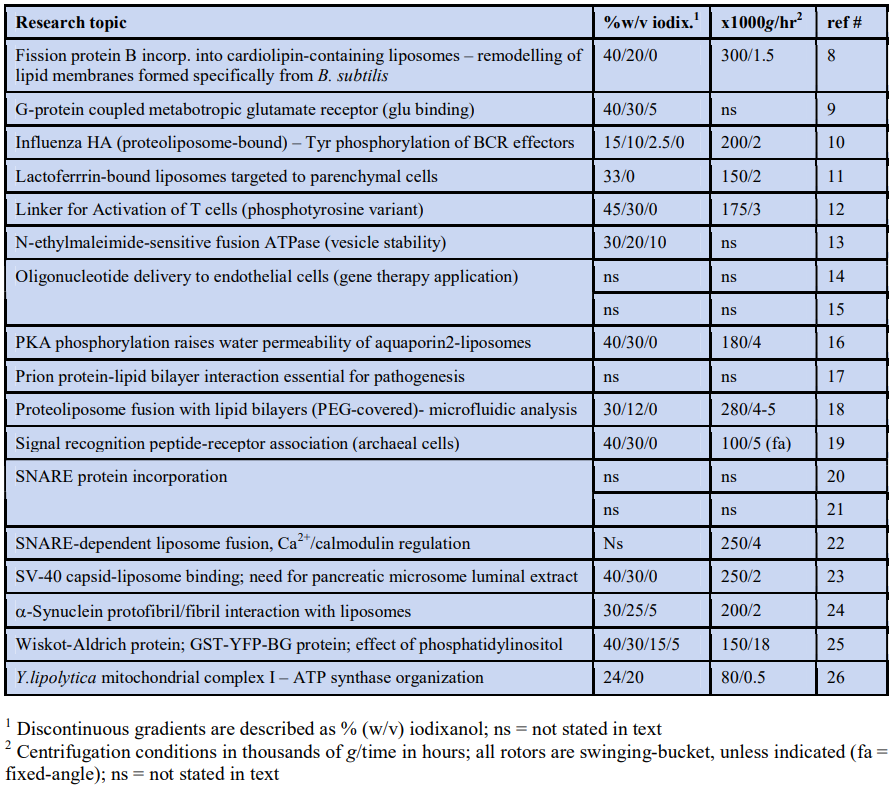
2.1 Table of published papers
The entries are listed alphabetically according to principal area of investigation. All of the papers report the use of flotation rather than sedimentation for purifying the proteoliposomes (the table continues on the next page).
2.2 References
1. Christis, C., and Munro, S. (2012) The small G protein Arl1 directs the trans-Golgi– specific targeting of the Arf1 exchange factors IG1 and BIG2 J. Cell Biol., 196, 327–335
2. Ling, Y., Stefan, C.J., MacGurn, J.A., Audhya, A. and Emr, S.D. (2012) The dual PH domain protein Opy1 functions as a sensor and modulator of PtdIns(4,5)P2 synthesis EMBO J., 31, 2882–2894
3. Jin, H., Roehl White, S., Shida, T., Schulz, S., Aguiar, M., Gygi, S.P., Bazan, J.F. and Nachury, M.V. (2010) The conserved Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins assemble a coat that traffics membrane proteins to cilia Cell 141, 1208–1219
4. Huang, W., Choi, W., Hu, W., Mi, N., Guo, Q., Ma, M., Liu, M., Tian, Y., Lu, P., Wang, F-L., Deng, H., Liu, L., Gao, N., Yu, L. and Shi, Y. (2012) Crystal structure and biochemical analyses reveal Beclin 1 as a novel membrane binding protein Cell Res., 22, 473-489
5. Bonander, N., Jamshad, M., Oberthur, D., Clare, M., Barwell, J., Hu, K., Farquhar, M.J., Stamataki, Z., Harris, H.J., Dierks, K., Dafforn, T.R., Betzel, C., McKeating, J.A. and Bill, R.M. (2013) Production, purification and characterization of recombinant, full-length human claudin-1 PloS One, 8: e64517
6. Perez, T.D., Nelson, W.J., Boxer, S.G. and Kam, L. (2005) E-Cadherin tethered to micropatterned supported lipid bilayers as a model for cell adhesion Langmuir, 21, 11963-11968
7. Volmer, R., van der Ploeg, K. and Ron, D. (2103)Membrane lipid saturation activates endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response transducers through their transmembrane domains Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 4628–4633
8. Doan, T., Coleman, J., Marquis, K.A., Meeske, A.J., Burton, B.M., Karatekin, E. and Rudner, D.Z. (2013) FisB mediates membrane fission during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis Genes Dev., 27, 322–334
9. Eroglu, C.A., Cronet, P., Panneels, V., Beaufils, P. and Sinning, I. (2002) Functional reconstitution of purified metatropic glutamate receptor expressed in the fly eye EMBO Rep., 3, 491-496
10. Lingwood, D., McTamney, P.M., Yassine, H.M., Whittle, J.R.R., Guo, X., Boyington, J.C., Wei, C-J. and Nabel, G.J. (2012) Structural and genetic basis for development of broadly neutralizing influenza antibodies Nature, 489, 566-570
11. Weeke-Klimp, A.H., Bartsch, M., Morselt, H.W.M., van Veen-Hof, I., Meijer, D.K.F., Scherphof, G.L. and Kamps, J.A.A.M. (2007) Targeting of stabilized plasmid lipid particles to hepatocytes in vivo by means of coupled lactoferrin J. Drug Target., 15, 585-594
12. Sangani, D., Venien-Bryan, C. and Harder, T. (2009) Phosphotyrosine-dependent in vitro reconstitution of recombinant LAT-nucleated multiprotein signalling complexes on liposomes Mol Membr. Biol., 26, 159- 170
13. Brugger, B., Nickel, W., Weber, T., Parlati, F., McNew, J.A., Rothman, J.E. and Sollner, T. (2000) Putative fusogenic activity of NSF is restricted to a lipid mixture whose coalescence is also triggered by other factors The EMBO J., 19, 1272-1278
14. Bartsch, M., Weeke-Klimp, A.H., Meijer, D.K.F., Scherphof, G.L. and Kamps, J.A.A.M. (2002) Massive and selective delivery of lipid-coated cationic lipoplexes of oligonucleotides targeted in vivo to hepatic endothelial cclls Pharm. Res., 19, 676-680
15. Bartsch, M., Weeke-Klimp, A.H., Morselt, H.W.M., Kimpfler, A., Asgeirsdottir, S.A., Schubert, R., Meijer, D.K.F., Scherphof, G.L. and Kamps, J.A.A.M. (2005) Optimized targeting of polyethylene glycolstabilized anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 oligonucleotide/lipid particles to liver sinusoidal endothelial cells Mol. Pharmacol., 67, 883-890
16. Eto, K., Noda, Y., Horikawa, S., Uchida, S. and Sasaki, S. (2010) Phosphorylation of aquaporin-2 regulates its water permeability J. Biol. Chem., 285, 40777-40784
17. Wang, F., Yin, S., Wang, X., Zha, L., Sy, M-S. and Ma, J. (2010) Role of the highly conserved middle region of prion protein (PrP) in PrP-lipid interaction Biochemistry, 49, 8169–8176
18. Karatekin, E. and Rothman, J.E. (2012) Fusion of single proteoliposomes with planar, cushioned bilayers in microfluidic flow cells Nat. Protoc., 7, 903-920
19. Moll, R.G. (2003) Protein-protein, protein-RNA and protein-lipid interactions of signal-recognition particle components in the hyperthermoacidophilic archeon Arcidianus ambivalens Biochem. J., 374, 247-254
20. Hu, K., Carroll, J., Fedorovich, S., Rickman, C., Sukhodub, A. and Davletov, B. (2002) Vesicular restriction of synaptobrevin suggests a role for calcium in membrane fusion Nature, 415, 646-650
21. Hu, K., Rickman, C., Carroll. J. and Davletov, B. (2004) A common mechanism for the regulation of vesicular SNAREs on phospholipid membranes Biochem. J., 377, 781-765
22. Di Giovanni, J., Iborra, C., Maulet, Y., Lévêque, C., El Far, O. and Seagar, M. (2010) Calcium-dependent regulation of SNARE-mediated membrane fusion by calmodulin J. Biol. Chem., 285, 23665–23675
23. Geiger, R., Andritschke, D., Friebe, S., Herzog, F., Luisoni, S., Heger, T. and Helenius, A. (2011) BAP31 and BiP are essential for dislocation of SV40 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol Nat. Cell Biol., 13, 1305-1314
24. Volles, M.J., Lee, S-L., Rochet, J-C., Shtilerman, M.D., Ding, T.T., Kessler, J.C. and Lansbury, P.T. (2001) Vesicle permeabilization by protofibrillar -synuclein: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease Biochemistry, 40, 7812-7819
25. Myers, S.A., Han, J.W., Lee, Y., Firtel, R.A. and Chung, C.Y.A. (2005) Dictyostelium homologue of WASP is required for polarized F-actin assembly during chemotaxis Mol. Biol. Cell, 16, 2191-2206
26. Davies, K.M., Strauss, M., Daum, B., Kief, J.H., Osiewacz, H.D., Rycovska, A., Zickermann, V. and Kühlbrandt, W. (2011) Macromolecular organization of ATP synthase and complex I in whole mitochondria Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 108, 14121-14126
3. Papers published since mid 2014
Titles are listed alphabetically by first author and include papers on DNA-liposomes Ref 6 describes the separation of particles on the basis of size.
1. Bian, X., Zhang, Z., Xiong, Q., De Camilli, P. and Lin, C. (2019) A programmable DNA-origami platform for studying lipid transfer between bilayers Nat. Chem. Biol., 830, 830–837
2. Chandrasekar, S. and Shan, S-O. (2017) Anionic phospholipids and the albino3 translocase activate signal recognition particle-receptor interaction during light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein targeting J. Biol. Chem., 292, 397–406
3. Chen, D., Ganesh, S., Wang, W. and Amiji, M. (2019) The role of surface chemistry in serum protein corona-mediated cellular delivery and gene silencing with lipid nanoparticles Nanoscale, 11, 8760–8775
4. Chu, N.K., Shabbir, W., Bove-Fenderson, E., Araman, C., Lemmens-Gruber, R., Harris, D.A. and Becker, C.F.W. (2014) A C-terminal membrane anchor affects the interactions of prion proteins with lipid membranes J. Biol. Chem., 289, 30144–30160
5. Cortesio, C.L., Lewellyn, E.B. and Drubin, D.G. (2015) Control of lipid organization and actin assembly during clathrin-mediated endocytosis by the cytoplasmic tail of the rhomboid protein Rbd2 Mol. Biol. Cell, 26, 1509-1522
6. Igel-Egalon, A., Laferrière, F., Moudjou, M., Jan Bohl, J., Mezache, M., Knäpple, T., Herzog, L., Reine, F. et al (2019) Early stage prion assembly involves two subpopulations with different quaternary structures and a secondary templating pathway Commun. Biol., 2: 363
7. Fogeron, M-L., Jirasko, V., Penzel, S., Paul, D., Montserret, R., Danis, C., Lacabanne, D., Badillo, A. et al (2016) Cell-free expression, purification, and membrane reconstitution for NMR studies of the nonstructural protein 4B from hepatitis C virus J. Biomol. NMR, 65, 87–98
8. Garcia-Diez, R., Gollwitzer, C., Krumrey, M. and Varga, Z. (2016) Size determination of a liposomal drug by small-angle X-ray scattering using continuous contrast variation Langmuir, 32, 772−778
9. Heo, P., Ramakrishnan, S., Coleman, J., Rothman, J.E., Fleury, J-B. and Pincet, F. (2019) Highly reproducible physiological asymmetric membrane with freely diffusing embedded proteins in a 3D-printed microfluidic setup Small, 15: 1900725
10. Liang, K., Li, N., Wang, X., Dai, J., Liu, P., Wang, C., Chen, X-W., Gao, N. and Xiao, J. (2018) Cryo-EM structure of human mitochondrial trifunctional protein Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, 7039–7044
11. Luisoni, S., Suomalainen, M., Boucke, K., Tanner, L.B., Wenk, M.R., Guan, X.L., Grzybek, M., Coskun, U. and Greber, U.F. (2015) Co-option of membrane wounding enables virus penetration into cells Cell Host Microbe, 18, 75–85
12. Pike, C.M., Boyer-Andersen, R., Kinch, L.N., Caplan, J.L. and Neunuebel, M.R. (2019) The Legionella effector RavD binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate and helps suppress endolysosomal maturation of the Legionella-containing vacuole J. Biol. Chem., 294, 6405–6415
13. Ramakrishnan, S., Gohlke, A., Li, F., Coleman, J., Xu, W., Rothman, J.E. and Pincet, F. (2018) Highthroughput monitoring of single vesicle fusion using free-standing membranes and automated analysis Langmuir, 34, 5849−5859
14. Rouvinski, A., Dejnirattisai, W., Guardado-Calvo, P., Vaney, M-C., Sharma, A., Duquerroy, S., Supasa, P., Wongwiwat, W. (2017) Covalently linked dengue virus envelope glycoprotein dimers reduce exposure of the immunodominant fusion loop epitope Nat. Comm., 8: 15411
15. Schuhmacher, J.S., Rossmann, F., Dempwolff, F., Knauer, C., Altegoer, F., Steinchen, W., Dörrich, A.K. et al (2015) MinD-like ATPase FlhG effects location and number of bacterial flagella during C-ring assembly Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 112, 3092-3097
16. Spencer, C., Bensing, B.A., Mishra, N.N. and Sullam, P.M. (2019) Membrane trafficking of the bacterial adhesin GspB and the accessory Sec transport machinery J. Biol. Chem., 294, 1502–1515
17. Springer, S., Malkus, P., Borchert, B., Wellbrock, U., Duden, R. and Schekman, R. (2014) Regulated oligomerization induces uptake of a membrane protein into COPII vesicles independent of its cytosolic tail Traffic, 15, 531–545
18. Waldhart, A.N., Dykstra, H., Peck, A.S., Boguslawski, E.A., Madaj, Z.B., Wen, J., Veldkamp, K. et al (2017) Phosphorylation of TXNIP by AKT mediates acute influx of glucose in response to insulin Cell Rep., 19, 2005–2013
19. Weaver, G.C., Villar, R.F., Kanekiyo, M., Nabel, G.J., Mascola, J.R. and Lingwood, D. (2016) In vitro reconstitution of B cell receptor–antigen interactions to evaluate potential vaccine candidates Nat. Protoc., 11, 193-213
20. Xu, W., Nathwani, B., Lin, C., Wang, J., Karatekin, E., Pincet, F., Shih, W. and Rothman, J.E. (2016) A programmable DNA origami platform to organize SNAREs for membrane fusion J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 4439−4447
21. Xu, W., Nathwani, B., Lin, C., Wang, J., Karatekin, E., Pincet, F., Shih, W. and Rothman, J.E. (2016) A programmable DNA origami platform to organize SNAREs for membrane fusion J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 4439-4447
22. Yang, Y., Wang, J., Shigematsu, H., Xu, W., Shih, W.M., Rothman, J.E. and Lin, C. (2016) Self-assembly of size-controlled liposomes on DNA nanotemplates Nature Chem., 8, 476-483
23. Ysselstein, D., Joshi, M., Mishra, V., Griggs, A.M., Asiago, J.M., McCabe, G.P., Stanciu, L.A., Post, C.B. and Rochet, J-C. (2015) Effects of impaired membrane interactions on α-synuclein aggregation and neurotoxicity Neurobiol. Dis., 79, 150–163
24. Zhang, Z., Yang, Y., Pincet, F., Llaguno, M.C. and Lin, C. (2017) Placing and shaping liposomes with reconfigurable DNA nanocages Nat. Chem., 9, 653-659
OptiPrep™ Reference List RM02; 7th edition, January 2020
